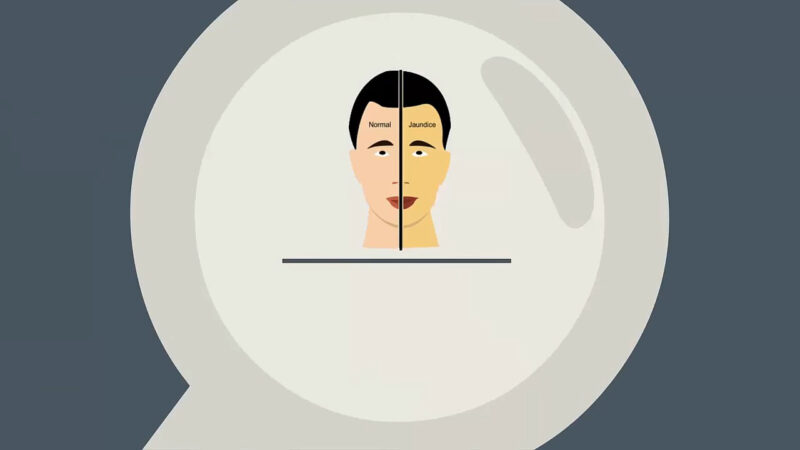
Jaundice is an ailment distinguished by the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, predominantly caused by the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood and body tissues. It’s pivotal to understand its various types, causes, signs, and possible treatments to implement a constructive approach to manage and prevent this condition.
Below is a thorough examination of jaundice, enlightening us about its diverse dimensions and implications. This is not a disease but rather a visible sign of an underlying disease process.
It occurs when there is too much bilirubin, a yellow-orange pigment, in the blood—causing the skin, whites of the eyes, and mucous membranes to turn yellow. Let’s delve into the basics of jaundice, providing insights into its symptoms and causes.
An unmistakable condition, easily identified by the distinctive yellowing of the skin and eyes. It’s essential to recognize this symptom early to determine the underlying cause and initiate appropriate management. This symptom is a signal from the body that there is an imbalance or disruption in the normal metabolism and excretion of bilirubin.
Symptoms
The primary symptoms of jaundice are a yellow discoloration of the skin and the eyes, coupled with pale-colored stools and dark-colored urine.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Pale colored stools
- Dark colored urine
It’s crucial to monitor these symptoms meticulously as they can be indicative of the progression and severity of jaundice, serving as an impetus for further diagnostic procedures and management strategies.
Causes
It can be classified into three main categories: pre-hepatic, hepatocellular, and post-hepatic, each relating to different parts of the physiological mechanism and pathology affecting them. The categorization is essential for understanding the genesis of jaundice, aiding in devising appropriate therapeutic interventions.
- Pre-hepatic Jaundice: Occurs due to an increased rate of haemolysis (breakdown of red blood cells). The causes include malaria, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and Gilbert syndrome.
- Hepatocellular Jaundice: Arises due to infections or exposure to harmful substances like alcohol disrupting the liver’s ability to process bilirubin.
- Post-hepatic Jaundice: Also called obstructive jaundice, it is caused by an interruption to the drainage of bile in the biliary system, commonly due to gallstones or pancreatic cancer.
The Role of Bilirubin
Bilirubin, a byproduct of the breakdown of red blood cells, plays a central role in the development of jaundice. Its accumulation can occur if red blood cells break down too early if there is faulty uptake, processing, or excretion of bilirubin by the liver cells, or if there is a blockage in the bile duct.
- The spleen can get overloaded if red blood cells break down too early, causing a build-up of bilirubin.
- Newborn babies can be temporarily jaundiced due to a lack of mature enzymes needed to process bilirubin.
- Alcoholism and exposure to other toxins and certain drugs can cause acute damage to the liver cells and affect the processing of bilirubin.
Understanding the mechanics of bilirubin processing and the reasons behind its build-up is crucial for grasping why and how jaundice develops in various physiological conditions.
Diagnosing
For a comprehensive diagnosis of jaundice, healthcare providers usually recommend a series of tests such as urine tests, blood tests, and other primary lab tests. These tests are crucial for assessing the levels of bilirubin, urobilinogen, and various enzymes and proteins, thereby allowing healthcare providers to pinpoint the underlying cause of jaundice.
- Urine Test: Measures levels of urobilinogen, a substance produced when bacteria break down bilirubin inside the digestive system.
- Blood Tests: Include measuring blood levels of enzymes found primarily in the liver, bilirubin levels, and protein levels, specifically total protein and albumin.
Timely and accurate diagnosis is indispensable in managing jaundice effectively and preventing any further complications that might arise due to the underlying conditions causing jaundice.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis
Timely diagnosis is crucial to initiate early treatment and manage the underlying condition causing jaundice effectively. It helps in preventing the progression of the disease and averting any complications that may arise due to delayed treatment.
- Early diagnosis aids in identifying the cause of jaundice promptly, allowing for timely intervention.
- It reduces the risk of complications and improves the overall prognosis of the condition.
Managing
 Managed by addressing its underlying causes and symptoms. The management strategy may vary depending on whether the jaundice is pre-hepatic, intra-hepatic, or post-hepatic.
Managed by addressing its underlying causes and symptoms. The management strategy may vary depending on whether the jaundice is pre-hepatic, intra-hepatic, or post-hepatic.
Addressing the specific type and cause is crucial in mitigating the effects and preventing further complications related to jaundice. Management focuses primarily on alleviating the root causes and the symptoms associated with jaundice.
By managing the symptoms and the underlying conditions effectively, the complications associated with jaundice can be significantly reduced, leading to better patient outcomes and improved quality of life.
Specific Management Strategies
- For Prehepatic, the focus is on preventing the rapid breakdown of red blood cells, utilizing medications to treat underlying infections, or blood transfusions for genetic blood disorders.
- Intra-hepatic requires prevention of further liver damage, potentially using anti-viral medications for infections or avoiding exposure to harmful substances.
- Post-hepatic usually necessitates surgery to unblock the bile duct system, sometimes requiring removal of the gallbladder or a section of the bile duct system or pancreas.
Implementing the appropriate management strategies promptly is pivotal to halt the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s overall condition.
Prevention
Prevention is the cornerstone in managing the risk of developing jaundice. It is pivotal to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and take precautionary measures such as moderating alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding high-risk behaviors.
- Moderate alcohol consumption to avoid exceeding the recommended daily amount.
- Maintain good hygiene and avoid potentially contaminated food/water to prevent infections.
- Vaccination against hepatitis A and hepatitis B can significantly reduce the risk of liver infections.
Adhering to these preventive measures and maintaining a balanced lifestyle can significantly minimize the risk of developing jaundice and ensure overall well-being and liver health.
Importance of Prevention
Preventing is vital as it’s not possible to prevent all cases of jaundice due to its varied causes and underlying conditions. Effective prevention strategies can mitigate the risk of developing and help in maintaining overall health.
- Adopting a proactive approach to prevention aids in the early detection and management of potential risk factors.
- Effective preventive measures can curtail the incidence of jaundice and contribute to enhanced liver function and overall health.
Addressing Newborns
Particularly common in newborns due to the immaturity of the liver. The lack of mature enzymes needed to process bilirubin often results in temporary jaundice in newborns, necessitating close monitoring and appropriate management strategies to ensure the well-being of the infant.
- The condition is generally temporary and often resolves itself as the baby’s liver develops the ability to process bilirubin more effectively.
- Close monitoring is essential to ensure that bilirubin levels do not reach a point where they could potentially cause harm to the newborn.
Early diagnosis and management are pivotal in addressing newborn jaundice, preventing any potential complications, and ensuring the healthy development of the infant.
Management and Prevention in Newborns
Managing and preventing jaundice in newborns primarily involves regular monitoring of bilirubin levels, phototherapy in cases of high bilirubin levels, and maintaining adequate hydration and nutrition.
- Phototherapy: It is a common and effective treatment for high bilirubin levels in newborns, where light waves are used to change bilirubin into byproducts that can be easily eliminated from the body.
- Adequate Nutrition: Ensuring that the newborn receives adequate nutrition and hydration is vital, as it helps in maintaining optimal bilirubin levels and preventing the occurrence of jaundice.
By focusing on preventive measures and proper management strategies, the complications associated with newborn jaundice can be substantially reduced, leading to improved infant health and well-being.
FAQ
Can jaundice be a symptom of cancer?
Yes, jaundice can be a symptom of cancer, particularly cancers that block the bile ducts such as pancreatic cancer and bile duct cancer, leading to obstructive jaundice.
How is it diagnosed in adults?
Beyond urine and blood tests, a healthcare provider may conduct imaging studies like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to examine the liver, bile ducts, and pancreas, especially when obstructive jaundice is suspected.
Can it occur in people without any liver condition?
Yes, jaundice can occur without liver conditions. Hemolytic anemia, a condition where red blood cells are broken down too quickly, can also cause jaundice, as it leads to an increased production of bilirubin.
Is it contagious?
Jaundice itself is not contagious, but the underlying conditions causing jaundice, like hepatitis A, B, or C, can be contagious.
Can it cause complications if left untreated?
Yes, if left untreated, the underlying conditions causing jaundice can lead to complications like liver failure, anemia, or chronic liver disease, depending on the cause and severity.
Can it be cured completely?
It can usually be resolved by treating the underlying condition causing it. The prognosis depends largely on the cause and severity of the jaundice.
Conclusion
Jaundice is a symptom rather than a disease, signifying an underlying health condition that requires immediate attention and management. Through a proper understanding of its symptoms, causes, and different types, along with accurate diagnosis, effective management strategies can be implemented to address the underlying condition causing jaundice.
The emphasis on preventive measures and lifestyle modifications further aids in reducing the risk of developing jaundice and maintaining optimal liver health. Lastly, special attention and care are required in cases of newborn jaundice to ensure the healthy growth and development of the infant.
If you’re interested in learning more about diseases, take a look at our article on Kala-azar.

